Obtaining political asylum in France
Obtaining political asylum in France is a complex and lengthy process. Only a qualified lawyer specializing in refugee and protection issues can create a refugee file that can be successfully defended in the special organization for refugees in France (OFPRA - OFPRA). If refugee status is denied at first instance, there is a special CNDA Refugee Court of Appeal that can reverse the OFPRA decision and recognize the applicant as a refugee.
Among European countries, France has always been considered a country where it is customary to protect human rights. Of all Western European countries, it is the leader in accepting refugees and ranks first in terms of the number of public human rights organizations. It is in France, in Strasbourg, that the European Court of Human Rights is located. In the minds of many people, France has always been and remains a hospitable and benevolent country to foreigners. For these and many other reasons, Russian refugees choose this particular country as their political asylum.
Among European countries, France has always been considered a country where it is customary to protect human rights. Of all Western European countries, it is the leader in accepting refugees and ranks first in terms of the number of public human rights organizations. It is in France, in Strasbourg, that the European Court of Human Rights is located. In the minds of many people, France has always been and remains a hospitable and benevolent country to foreigners. For these and many other reasons, Russian refugees choose this particular country as their political asylum.

The information below is for public institutions only. It is they who deal with the consideration of applications for political asylum. There are many agencies and associations that people should interact with during the asylum procedure.
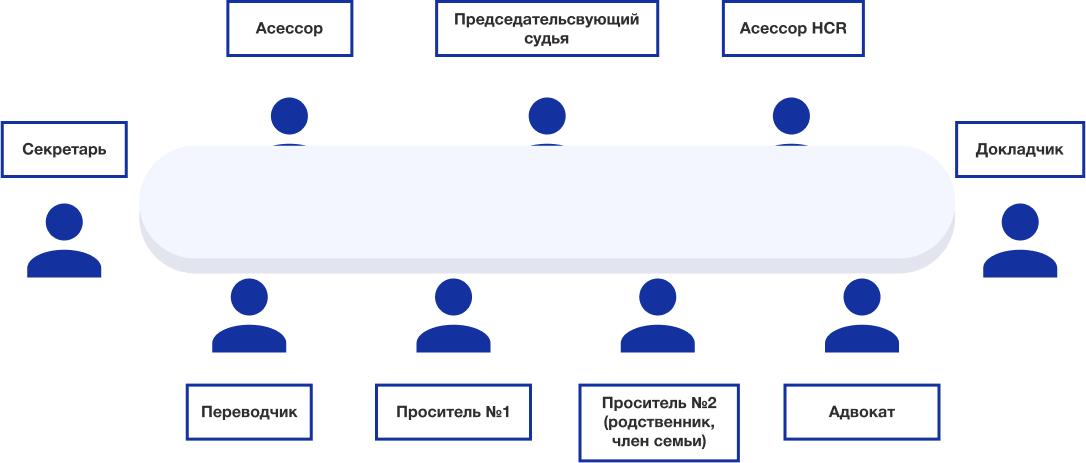
Who is involved in the examination of asylum applications?

CNDA will review your case and analyze the reasons for OFPRA's denial
The court will ask for additional documents or information according to your story. In the CNDA, both the asylum seeker and the lawyer are given the opportunity to prove that the OFPRA made the wrong decision. First, the rapporteur reads your case, and then the judge and assessors take turns asking additional questions to the asylum seeker. After that, the lawyer shares his thoughts. During the hearing, you need to be especially vigilant, accurate and confident in your answers, as the chairman of the hearing will ask specific questions that may not be connected chronologically. If you haven't had time to learn French yet and you don't speak French well enough, you will be provided with an interpreter free of charge. The French state will also pay for the lawyer's fees (aide juridictionnelle). In the CNDA, an asylum seeker is assisted by a free lawyer in 60% of cases. Of course, it is better to hire a paid lawyer, because state lawyers face such a problem as lack of time. Often they simply do not have the opportunity to meet with asylum seekers until the very meeting. In addition, there is always a risk that the lawyer does not fully know your situation, the reason for OFPRA's refusal, or is not an expert on your topic at all.
Different types of asylum procedures - classical or accelerated? The OFPRA is responsible for examining asylum applications under both the regular (classic) and accelerated procedures. In both cases, the petition itself is theoretically treated in the same way. There is a big difference in terms of consideration of applications. OFPRA makes a decision within 2 weeks in the case of an expedited procedure, instead of 6 months in the case of a classic procedure. Persons who arrived from a country included in the list of so-called. "safe countries" are placed under the fast track procedure. The same procedure applies to persons who request a review of their case after a refusal decision, those who provided false documents, as well as those who refused to be fingerprinted. It may happen that OFPRA decides to cancel the accelerated procedure, for example, for members of the same family. For example, among our clients there were two sisters, one of whom underwent a classic procedure, and the other an accelerated one. Ultimately, the cases of both sisters were considered under the classical procedure.
Different types of asylum procedures - classical or accelerated? The OFPRA is responsible for examining asylum applications under both the regular (classic) and accelerated procedures. In both cases, the petition itself is theoretically treated in the same way. There is a big difference in terms of consideration of applications. OFPRA makes a decision within 2 weeks in the case of an expedited procedure, instead of 6 months in the case of a classic procedure. Persons who arrived from a country included in the list of so-called. "safe countries" are placed under the fast track procedure. The same procedure applies to persons who request a review of their case after a refusal decision, those who provided false documents, as well as those who refused to be fingerprinted. It may happen that OFPRA decides to cancel the accelerated procedure, for example, for members of the same family. For example, among our clients there were two sisters, one of whom underwent a classic procedure, and the other an accelerated one. Ultimately, the cases of both sisters were considered under the classical procedure.
If it turns out that the case is more complicated than it seems, the applicant may also revert to the classical procedure at the discretion of the OFPRA. We had a client with dual citizenship, one citizenship of a safe country and the other not. His case required a more in-depth study, so it was decided to transfer his consideration to the classical procedure. Technically, an expedited procedure could be seen as a penalty. The consequences are primarily felt at the CNDA level when the OFPRA has denied an asylum seeker and the asylum seeker is filing an appeal with the CNDA. Unlike a traditional asylum seeker, who would have more time to write a defense and collect evidence, in this case you will have about two weeks and your CNDA case will be heard in an expedited manner by only one judge (juge unique) without assessors. According to a 2018 OFPRA report, last year 24 asylum applications under the accelerated procedure were transferred to the regular classical procedure.
Do you feel a bit overwhelmed by such a large flow of information?
To make it easier to understand the asylum procedure in France, take a look at this diagram. We hope it helps you understand the main points.
The procedure for obtaining political asylum

PADA
PADA are platforms for asylum seekers. Each department has at least one such platform. Some of them sometimes have several offices in each department. They are responsible for receiving newly arrived migrants and help arrange the first meeting in the prefecture.
PADA are platforms for asylum seekers. Each department has at least one such platform. Some of them sometimes have several offices in each department. They are responsible for receiving newly arrived migrants and help arrange the first meeting in the prefecture.

OFII (French Office of Immigration and Integration)
The OFII will ask you to answer a list of questions to determine if you need special admissions. The role of this department is both to ensure the conditions for the reception of migrants during the consideration of their asylum application, and to integrate persons who have already received protection (in particular, by signing a republican integration contract, which opens the right to 200 hours of French lessons for migrants). OFII is in close cooperation with OFPRA.
The OFII will ask you to answer a list of questions to determine if you need special admissions. The role of this department is both to ensure the conditions for the reception of migrants during the consideration of their asylum application, and to integrate persons who have already received protection (in particular, by signing a republican integration contract, which opens the right to 200 hours of French lessons for migrants). OFII is in close cooperation with OFPRA.

OFPRA (French Office of Immigration and Integration)
This public institution is especially important for the asylum seeker as it makes the decisions in the process of examining your application. This is where you will send all the documents related to your case. First, you will need to describe your personal situation on several pages, while remaining as accurate and concise as possible. You do not need to tell everything, you need to be able to highlight in your story only the most important facts that you can document.
To do this, you can use the links to the press or video materials. But do not forget that they should be used as documentary evidence of the situation you experienced, and not the general situation in the country. Applicants are then interviewed individually by an officer of protection (officier de protection) who will review your case. You will need to carefully prepare for the interview, as a refugee officer will ask you specific questions, often of a personal nature. During the interview, you should not be nervous or overly nervous, this may be misinterpreted by an OFPRA employee.
It should be noted that many asylum seekers have quite good memories of interacting with OFPRA employees. You must clearly know your history, avoid contradictions between your written story and answers to questions from a management officer. It should be noted that many asylum seekers have quite good memories of interacting with OFPRA employees. You must clearly know your history, avoid contradictions between your written story and answers to questions from a management officer.
If you do not speak French, you will be provided with the assistance of an interpreter. The OFPRA institution itself is located in Fontenoy-sous-Bois (in the suburbs of Paris). All asylum seekers in France pass through it, wherever they live in Marseille, Nantes, Strasbourg or in any other city in France.
This public institution is especially important for the asylum seeker as it makes the decisions in the process of examining your application. This is where you will send all the documents related to your case. First, you will need to describe your personal situation on several pages, while remaining as accurate and concise as possible. You do not need to tell everything, you need to be able to highlight in your story only the most important facts that you can document.
To do this, you can use the links to the press or video materials. But do not forget that they should be used as documentary evidence of the situation you experienced, and not the general situation in the country. Applicants are then interviewed individually by an officer of protection (officier de protection) who will review your case. You will need to carefully prepare for the interview, as a refugee officer will ask you specific questions, often of a personal nature. During the interview, you should not be nervous or overly nervous, this may be misinterpreted by an OFPRA employee.
It should be noted that many asylum seekers have quite good memories of interacting with OFPRA employees. You must clearly know your history, avoid contradictions between your written story and answers to questions from a management officer. It should be noted that many asylum seekers have quite good memories of interacting with OFPRA employees. You must clearly know your history, avoid contradictions between your written story and answers to questions from a management officer.
If you do not speak French, you will be provided with the assistance of an interpreter. The OFPRA institution itself is located in Fontenoy-sous-Bois (in the suburbs of Paris). All asylum seekers in France pass through it, wherever they live in Marseille, Nantes, Strasbourg or in any other city in France.

CNDA (Refugee Court of Appeal)
There is a possibility that you will be denied OFPRA management. In this case, you will have the opportunity to apply to the National Asylum Court (CNDA) and appeal against the OFPRA decision. Below you will find a rough outline of the CNDA Hearing Participants to give you a general idea of how your hearing will work.
There is a possibility that you will be denied OFPRA management. In this case, you will have the opportunity to apply to the National Asylum Court (CNDA) and appeal against the OFPRA decision. Below you will find a rough outline of the CNDA Hearing Participants to give you a general idea of how your hearing will work.

Filing an application
Appeal to the primary admission structure (SPADA) at the place of stay to receive a referral to the Prefecture, 3-10 days from the date of application.
Appeal to the primary admission structure (SPADA) at the place of stay to receive a referral to the Prefecture, 3-10 days from the date of application.

Reception at the Prefecture
The prefecture will take fingerprints, determine the type of procedure (regular, fast track, Dublin), issue a refugee certificate and an OFPRA form, and forward to OFII for social assistance.
The prefecture will take fingerprints, determine the type of procedure (regular, fast track, Dublin), issue a refugee certificate and an OFPRA form, and forward to OFII for social assistance.

Applying to OFPRA
Within 21 days after admission to the Prefecture. You must submit a completed form and attach supporting documents.
Within 21 days after admission to the Prefecture. You must submit a completed form and attach supporting documents.

Dossier review
OFPRA staff will conduct interviews and analyze all submissions. You may be accompanied by an interpreter and/or a lawyer.
OFPRA staff will conduct interviews and analyze all submissions. You may be accompanied by an interpreter and/or a lawyer.

Judgment
In case of a positive decision, civil status documents are issued. The refusal can be challenged with the CNDA.
In case of a positive decision, civil status documents are issued. The refusal can be challenged with the CNDA.

Appeal to CNDA
OFPRA's decision can be appealed within 1 month. The CNDA may reverse the OFPRA decision or confirm the denial.
It is quite obvious that the requirements for the procedure for obtaining refugee status are very high and there are many nuances in it, ignorance of which can cause irreparable damage to an asylum seeker. Language, legal, legislative and many other barriers are often a deterrent and sometimes stop applicants halfway to the goal. To prevent such a situation, you need to seek help from specialists and experts who will advise you on any issue related to the granting of political asylum at each stage of obtaining it.
Contact us, and we will be able to clarify the situation you do not understand and we will become your assistant when interacting with all of the above administrative structures.
OFPRA's decision can be appealed within 1 month. The CNDA may reverse the OFPRA decision or confirm the denial.
It is quite obvious that the requirements for the procedure for obtaining refugee status are very high and there are many nuances in it, ignorance of which can cause irreparable damage to an asylum seeker. Language, legal, legislative and many other barriers are often a deterrent and sometimes stop applicants halfway to the goal. To prevent such a situation, you need to seek help from specialists and experts who will advise you on any issue related to the granting of political asylum at each stage of obtaining it.
Contact us, and we will be able to clarify the situation you do not understand and we will become your assistant when interacting with all of the above administrative structures.

Come to live in France.
The main values of French society and the Republic.
Core Values of French Society and the Republic Each year, France welcomes more than 100,000 non-European Union foreigners from all regions of the world who seek permanent residence in France. France is a multi-million nation with a rich history and culture. The name of the country is synonymous with the fundamental values to which the French are committed. Similar values exist in all countries and allow people to live together within the same society: some of the values are universal and common to all mankind, others relate only to the culture of one country, being the result of the history that a particular territory has lived. They are so important that, when applied to people of different backgrounds, they unite them around common rules. These values are expressed in the motto of the French Republic: liberty, equality, fraternity.
Read completely
The main values of French society and the Republic.
Core Values of French Society and the Republic Each year, France welcomes more than 100,000 non-European Union foreigners from all regions of the world who seek permanent residence in France. France is a multi-million nation with a rich history and culture. The name of the country is synonymous with the fundamental values to which the French are committed. Similar values exist in all countries and allow people to live together within the same society: some of the values are universal and common to all mankind, others relate only to the culture of one country, being the result of the history that a particular territory has lived. They are so important that, when applied to people of different backgrounds, they unite them around common rules. These values are expressed in the motto of the French Republic: liberty, equality, fraternity.
Read completely
Приехать жить во Францию.
Главные ценности французского общества и Республики.
Главные ценности французского общества и Республики.
Главные ценности французского общества и Республики Каждый год Франция принимает более 100 000 иностранцев, являющихся гражданами стран, не относящихся к Европейскому союзу, из всех регионов мира, целью которых является постоянное проживание на территории Франции. Франция — это многомиллионная нация с богатой историей и культурой. Название страны является синонимом фундаментальных ценностей, которым привержены французы. Подобные ценности существуют во всех странах и позволяют людям жить вместе в рамках одного общества: некоторые из ценностей универсальные и общие для всего человечества, другие относятся только к культуре одной страны, являясь результатом истории, которую прожила отдельно взятая территория. Они настолько важны, что, применяясь к людям разного происхождения, они объединяют их вокруг общих правил. Эти ценности выражены в девизе Французской Республики: свобода, равенство, братство.
Также они включают в себя и светскость. Эти ценности соответствуют принципам, выраженным в законе, который обязаны уважать все — как французские граждане, так и любой человек, постоянно или временно проживающий во Франции. Законы принимаются демократическими институтами, которые избираются народом. Институты призваны организовывать отношения между гражданами в повседневной жизни на основе этих ценностей и принципов.
Это касается не только абстрактных понятий: эти ценности имеют практические влияние на повседневную жизнь посредством прав и обязанностей граждан и резидентов. Франция уделяет особое внимание качеству приема, оказываемого иностранцам, желающим надолго остаться на ее территории. Именно поэтому был разработан персонализированный процесс республиканской интеграции. Благодаря этому процессу каждый человек может принимать права и обязанности, которые применяются ко всем на территории Франции.
Приехать жить во Францию Главные ценности французского общества и Республики Франция сегодня — это результат долгой истории, событий и выбора, который делал французский народ на протяжении времен. Она была сформирована борьбой за демократические ценности: свободу, равенство и братство. Франция также особенно привержена принципу светскости, рамки которого были установлены законом от 9 сентября 1905 г., оговаривающим разделение церквей и государства. Эти ценности являются фундаментом всех законов и всех институтов, организующих жизнь страны.
Соблюдение законов и осознание гражданского долга являются необходимыми качествами для жизни в обществе. Республика гарантирует равенство и права любому человеку, проживающему во Франции. Права неотделимы от обязанностей. Жить во Франции — значит иметь не только права, но и обязанности. ü Ценности Франции Свобода, равенство и братство являются ценностями, берущими начало из Декларации прав человека и гражданина от 26 августа 1789 г. Этот основополагающий документ Французской Республики определяет права и свободы каждого индивидуума и закрепляет принцип равенства между мужчинам и женщинами, гарантированный Конституцией 1958 г. Эти ценности лежат в основе Республики и французского права и являются источником правил, выраженных в правах, обязанностях и запретах.
Свобода Гарантированы фундаментальные свободы: свобода мысли, свобода вероисповедания, свобода самовыражения, свобода собраний, свобода вступления в брак и т. д. В 1880-х годах закон гарантировал свободу прессы. Народное образование стало обязательным, а общественные школы стали бесплатными и светскими. Равенство Все граждане имеют одинаковые права и обязанности, независимо от пола, происхождения, вероисповедания, взглядов или сексуальной ориентации. Женщины и мужчины обладают равными правами и обязанностями во всех сферах. Братство Франция была основана на желании французских граждан жить вместе. Франция представляет собой социальную республику, которая гарантирует солидарность, вносит вклад в консолидацию общества и служит интересам общества. Работающие граждане обладают правами, гарантированными им законом, а система социальной 5 Приехать жить во Францию Главные ценности французского общества и Республики защиты позволяет предотвратить различные риски, которые могут возникнуть в жизни человека.
Светскость Франция является светской республикой, которая гарантирует свободу вероисповедания и защищает свободу совести. Светскость — это разделение церквей и государства. Государство не зависит от религий и не содействует ни одной из церквей. Таким образом, государство сохраняет нейтральное отношение и не осуществляет финансирование ни одного из религиозных культов. Подобное разделение создает залог свободы совести, т. е. свободы вероисповедания, которая охраняется государством. Это означает, что до тех пор, пока не нарушается общественный порядок, французское государство гарантирует каждому возможность соблюдать религиозные обряды в соответствии с действующими текстами выбранной человеком религии, менять вероисповедание, или вообще не соотносить себя с какой-либо из религий. Вероисповедание относится к частной жизни человека, и каждый свободен в своем выборе — верить или нет — и может принимать ту религию, которую пожелает. ü Французская Республика Франция является единой и неделимой республикой, что подразумевает наличие единой территории, одного официального языка и единого закона, который применим к каждому.
В состав Франции на сегодняшний день входит 13 регионов, 101 департамент и более 35 000 коммун. Территория Франции включает метрополию и простирается на восемь заморских территорий. Франция — это демократическая республика. Ее принцип — народная власть, осуществляемая народом и в интересах народа. Выборы политических деятелей проводятся на основании всеобщего избирательного права, то есть все граждане, как мужчины, так и женщины, обладают правом голоса. Франция является правовым государством, основанным на законах, которые должны соблюдаться всеми, включая государственную власть. Организация государства определяется особым документом — конституцией. Действующая конституция является конституцией Пятой республики, принятой в 1958 г. Независимость судебной власти гарантирована.
Приехать жить во Францию Главные ценности французского общества и Республики Политические партии могут свободно создаваться и осуществлять свою деятельность. Наши государственные институты основаны на принципе разделения исполнительной, законодательной и судебной власти. Исполнительная власть Президент Республики избирается всеобщим прямым голосованием на пятилетний срок. Он назначает премьер-министра, а затем, по предложению последнего, назначает членов правительства. Законодательная власть Парламент, состоящий из национальной ассамблеи и сената, принимает законы и контролирует работу правительства. Депутаты национальной ассамблеи избираются каждые пять лет на парламентских выборах, а сенаторы избираются на всеобщих непрямых выборах и получают мандат на шесть лет. Судебная власть Судебная власть осуществляется судами. В случае нарушения закона суд назначает наказание в виде заключения под стражу или иное наказание, предусмотренное законом. Судебная власть решает споры между физическими или юридическими лицами, а также споры между гражданами и государством. Этот информационный буклет предназначен для лиц, желающих получить вид на жительство. После получения этого документа они могут обосноваться во Франции на продолжительное время и подписать договор о республиканской интеграции1 . Этот буклет, разработанный Министерством внутренних дел (Дирекцией по вопросам приема и сопровождения иностранцев и гражданства), является самым первым этапом в процессе интеграции. Благодаря этому буклету вы получите представление о принципе работы и организации французского общества, основу которого составляют республиканские ценности. В частности, в нем перечислены формальности, которые 1Это не относится к лицам, которые не должны подписывать договор о республиканской интеграции, в частности, к лицам, которые уже получили вид на жительство в качестве посетителя, студента, стажера, временно откомандированного лица, и лицам, получившим «паспорт талантливого специалиста» (статья 1 закона о правах иностранцев во Франции от 7 марта 2016 г.).
Приехать жить во Францию Главные ценности французского общества и Республики необходимо уладить перед отъездом, и документы, которые потребуются для осуществления необходимых действий после приезда во Францию. В буклете также представлена полезная информация о повседневной жизни, после ознакомления с которой вам будет проще интегрироваться в любую сферу и разделить ценности, объединяющие всех живущих во Франции, будь то французы или иностранцы.
С более подробной информацией вы можете ознакомиться здесь:
Также они включают в себя и светскость. Эти ценности соответствуют принципам, выраженным в законе, который обязаны уважать все — как французские граждане, так и любой человек, постоянно или временно проживающий во Франции. Законы принимаются демократическими институтами, которые избираются народом. Институты призваны организовывать отношения между гражданами в повседневной жизни на основе этих ценностей и принципов.
Это касается не только абстрактных понятий: эти ценности имеют практические влияние на повседневную жизнь посредством прав и обязанностей граждан и резидентов. Франция уделяет особое внимание качеству приема, оказываемого иностранцам, желающим надолго остаться на ее территории. Именно поэтому был разработан персонализированный процесс республиканской интеграции. Благодаря этому процессу каждый человек может принимать права и обязанности, которые применяются ко всем на территории Франции.
Приехать жить во Францию Главные ценности французского общества и Республики Франция сегодня — это результат долгой истории, событий и выбора, который делал французский народ на протяжении времен. Она была сформирована борьбой за демократические ценности: свободу, равенство и братство. Франция также особенно привержена принципу светскости, рамки которого были установлены законом от 9 сентября 1905 г., оговаривающим разделение церквей и государства. Эти ценности являются фундаментом всех законов и всех институтов, организующих жизнь страны.
Соблюдение законов и осознание гражданского долга являются необходимыми качествами для жизни в обществе. Республика гарантирует равенство и права любому человеку, проживающему во Франции. Права неотделимы от обязанностей. Жить во Франции — значит иметь не только права, но и обязанности. ü Ценности Франции Свобода, равенство и братство являются ценностями, берущими начало из Декларации прав человека и гражданина от 26 августа 1789 г. Этот основополагающий документ Французской Республики определяет права и свободы каждого индивидуума и закрепляет принцип равенства между мужчинам и женщинами, гарантированный Конституцией 1958 г. Эти ценности лежат в основе Республики и французского права и являются источником правил, выраженных в правах, обязанностях и запретах.
Свобода Гарантированы фундаментальные свободы: свобода мысли, свобода вероисповедания, свобода самовыражения, свобода собраний, свобода вступления в брак и т. д. В 1880-х годах закон гарантировал свободу прессы. Народное образование стало обязательным, а общественные школы стали бесплатными и светскими. Равенство Все граждане имеют одинаковые права и обязанности, независимо от пола, происхождения, вероисповедания, взглядов или сексуальной ориентации. Женщины и мужчины обладают равными правами и обязанностями во всех сферах. Братство Франция была основана на желании французских граждан жить вместе. Франция представляет собой социальную республику, которая гарантирует солидарность, вносит вклад в консолидацию общества и служит интересам общества. Работающие граждане обладают правами, гарантированными им законом, а система социальной 5 Приехать жить во Францию Главные ценности французского общества и Республики защиты позволяет предотвратить различные риски, которые могут возникнуть в жизни человека.
Светскость Франция является светской республикой, которая гарантирует свободу вероисповедания и защищает свободу совести. Светскость — это разделение церквей и государства. Государство не зависит от религий и не содействует ни одной из церквей. Таким образом, государство сохраняет нейтральное отношение и не осуществляет финансирование ни одного из религиозных культов. Подобное разделение создает залог свободы совести, т. е. свободы вероисповедания, которая охраняется государством. Это означает, что до тех пор, пока не нарушается общественный порядок, французское государство гарантирует каждому возможность соблюдать религиозные обряды в соответствии с действующими текстами выбранной человеком религии, менять вероисповедание, или вообще не соотносить себя с какой-либо из религий. Вероисповедание относится к частной жизни человека, и каждый свободен в своем выборе — верить или нет — и может принимать ту религию, которую пожелает. ü Французская Республика Франция является единой и неделимой республикой, что подразумевает наличие единой территории, одного официального языка и единого закона, который применим к каждому.
В состав Франции на сегодняшний день входит 13 регионов, 101 департамент и более 35 000 коммун. Территория Франции включает метрополию и простирается на восемь заморских территорий. Франция — это демократическая республика. Ее принцип — народная власть, осуществляемая народом и в интересах народа. Выборы политических деятелей проводятся на основании всеобщего избирательного права, то есть все граждане, как мужчины, так и женщины, обладают правом голоса. Франция является правовым государством, основанным на законах, которые должны соблюдаться всеми, включая государственную власть. Организация государства определяется особым документом — конституцией. Действующая конституция является конституцией Пятой республики, принятой в 1958 г. Независимость судебной власти гарантирована.
Приехать жить во Францию Главные ценности французского общества и Республики Политические партии могут свободно создаваться и осуществлять свою деятельность. Наши государственные институты основаны на принципе разделения исполнительной, законодательной и судебной власти. Исполнительная власть Президент Республики избирается всеобщим прямым голосованием на пятилетний срок. Он назначает премьер-министра, а затем, по предложению последнего, назначает членов правительства. Законодательная власть Парламент, состоящий из национальной ассамблеи и сената, принимает законы и контролирует работу правительства. Депутаты национальной ассамблеи избираются каждые пять лет на парламентских выборах, а сенаторы избираются на всеобщих непрямых выборах и получают мандат на шесть лет. Судебная власть Судебная власть осуществляется судами. В случае нарушения закона суд назначает наказание в виде заключения под стражу или иное наказание, предусмотренное законом. Судебная власть решает споры между физическими или юридическими лицами, а также споры между гражданами и государством. Этот информационный буклет предназначен для лиц, желающих получить вид на жительство. После получения этого документа они могут обосноваться во Франции на продолжительное время и подписать договор о республиканской интеграции1 . Этот буклет, разработанный Министерством внутренних дел (Дирекцией по вопросам приема и сопровождения иностранцев и гражданства), является самым первым этапом в процессе интеграции. Благодаря этому буклету вы получите представление о принципе работы и организации французского общества, основу которого составляют республиканские ценности. В частности, в нем перечислены формальности, которые 1Это не относится к лицам, которые не должны подписывать договор о республиканской интеграции, в частности, к лицам, которые уже получили вид на жительство в качестве посетителя, студента, стажера, временно откомандированного лица, и лицам, получившим «паспорт талантливого специалиста» (статья 1 закона о правах иностранцев во Франции от 7 марта 2016 г.).
Приехать жить во Францию Главные ценности французского общества и Республики необходимо уладить перед отъездом, и документы, которые потребуются для осуществления необходимых действий после приезда во Францию. В буклете также представлена полезная информация о повседневной жизни, после ознакомления с которой вам будет проще интегрироваться в любую сферу и разделить ценности, объединяющие всех живущих во Франции, будь то французы или иностранцы.
С более подробной информацией вы можете ознакомиться здесь:
- Декларация прав человека и гражданина 1789 г.: https://www.legifrance.gouv.fr/Droit-francais/Constitution/Declaration-des-Droits-de-lHomme-et-du-Citoyen-de-1789
- Закон 1905 г. о разделении церквей и государства: https://www.legifrance.gouv.fr/affichTexte.do?cidTexte=LEGITEXT000006070169&dateText e=20080306
- Конституция Пятой Республики 1958 г.: http://www.conseil-constitutionnel.fr/conseilconstitutionnel/francais/la-constitution/la-constitution-du-4-octobre-1958/preambule-dela-constitution-du-27-octobre-1946.5077.html

We are in touch daily
all days from 9:00 to 23:00

Anonymously and confidentially
Send us a message

Registration form: «Associations loi du 1er juillet 1901».
RNA registration number: W641013804
Address: France, 14 rue Jacques Laffitte 64100 Bayonne.
Individual tax number N° DE PARUTION: 20230008
Name of the Association: «ASYLUM RESEARCH & GLOBAL ASSISTANCE»
E-mail address: asilepolitfrance@gmail.com
Phone number: +33782070855
RNA registration number: W641013804
Address: France, 14 rue Jacques Laffitte 64100 Bayonne.
Individual tax number N° DE PARUTION: 20230008
Name of the Association: «ASYLUM RESEARCH & GLOBAL ASSISTANCE»
E-mail address: asilepolitfrance@gmail.com
Phone number: +33782070855
Политика в отношении обработки персональных данных
1. Общие положения
Настоящая политика обработки персональных данных составлена в соответствии с требованиями Федерального закона от 27.07.2006. №152-ФЗ «О персональных данных» (далее - Закон о персональных данных) и определяет порядок обработки персональных данных и меры по обеспечению безопасности персональных данных, предпринимаемые RELOCATOR (далее – Оператор).
1.1. Оператор ставит своей важнейшей целью и условием осуществления своей деятельности соблюдение прав и свобод человека и гражданина при обработке его персональных данных, в том числе защиты прав на неприкосновенность частной жизни, личную и семейную тайну.
1.2. Настоящая политика Оператора в отношении обработки персональных данных (далее – Политика) применяется ко всей информации, которую Оператор может получить о посетителях веб-сайта https://relocator.world.
2. Основные понятия, используемые в Политике
2.1. Автоматизированная обработка персональных данных – обработка персональных данных с помощью средств вычислительной техники.
2.2. Блокирование персональных данных – временное прекращение обработки персональных данных (за исключением случаев, если обработка необходима для уточнения персональных данных).
2.3. Веб-сайт – совокупность графических и информационных материалов, а также программ для ЭВМ и баз данных, обеспечивающих их доступность в сети интернет по сетевому адресу https://relocator.world.
2.4. Информационная система персональных данных — совокупность содержащихся в базах данных персональных данных, и обеспечивающих их обработку информационных технологий и технических средств.
2.5. Обезличивание персональных данных — действия, в результате которых невозможно определить без использования дополнительной информации принадлежность персональных данных конкретному Пользователю или иному субъекту персональных данных.
2.6. Обработка персональных данных – любое действие (операция) или совокупность действий (операций), совершаемых с использованием средств автоматизации или без использования таких средств с персональными данными, включая сбор, запись, систематизацию, накопление, хранение, уточнение (обновление, изменение), извлечение, использование, передачу (распространение, предоставление, доступ), обезличивание, блокирование, удаление, уничтожение персональных данных.
2.7. Оператор – государственный орган, муниципальный орган, юридическое или физическое лицо, самостоятельно или совместно с другими лицами организующие и (или) осуществляющие обработку персональных данных, а также определяющие цели обработки персональных данных, состав персональных данных, подлежащих обработке, действия (операции), совершаемые с персональными данными.
2.8. Персональные данные – любая информация, относящаяся прямо или косвенно к определенному или определяемому Пользователю веб-сайта https://relocator.world/.
2.9. Персональные данные, разрешенные субъектом персональных данных для распространения, - персональные данные, доступ неограниченного круга лиц к которым предоставлен субъектом персональных данных путем дачи согласия на обработку персональных данных, разрешенных субъектом персональных данных для распространения в порядке, предусмотренном Законом о персональных данных (далее - персональные данные, разрешенные для распространения).
2.10. Пользователь – любой посетитель веб-сайта https://relocator.world/.
2.11. Предоставление персональных данных – действия, направленные на раскрытие персональных данных определенному лицу или определенному кругу лиц.
2.12. Распространение персональных данных – любые действия, направленные на раскрытие персональных данных неопределенному кругу лиц (передача персональных данных) или на ознакомление с персональными данными неограниченного круга лиц, в том числе обнародование персональных данных в средствах массовой информации, размещение в информационно-телекоммуникационных сетях или предоставление доступа к персональным данным каким-либо иным способом.
2.13. Трансграничная передача персональных данных – передача персональных данных на территорию иностранного государства органу власти иностранного государства, иностранному физическому или иностранному юридическому лицу.
2.14. Уничтожение персональных данных – любые действия, в результате которых персональные данные уничтожаются безвозвратно с невозможностью дальнейшего восстановления содержания персональных данных в информационной системе персональных данных и (или) уничтожаются материальные носители персональных данных.
3. Основные права и обязанности Оператора
3.1. Оператор имеет право:
– получать от субъекта персональных данных достоверные информацию и/или документы, содержащие персональные данные;
– в случае отзыва субъектом персональных данных согласия на обработку персональных данных Оператор вправе продолжить обработку персональных данных без согласия субъекта персональных данных при наличии оснований, указанных в Законе о персональных данных;
– самостоятельно определять состав и перечень мер, необходимых и достаточных для обеспечения выполнения обязанностей, предусмотренных Законом о персональных данных и принятыми в соответствии с ним нормативными правовыми актами, если иное не предусмотрено Законом о персональных данных или другими федеральными законами.
3.2. Оператор обязан:
– предоставлять субъекту персональных данных по его просьбе информацию, касающуюся обработки его персональных данных;
– организовывать обработку персональных данных в порядке, установленном действующим законодательством РФ;
– отвечать на обращения и запросы субъектов персональных данных и их законных представителей в соответствии с требованиями Закона о персональных данных;
– сообщать в уполномоченный орган по защите прав субъектов персональных данных по запросу этого органа необходимую информацию в течение 30 дней с даты получения такого запроса;
– публиковать или иным образом обеспечивать неограниченный доступ к настоящей Политике в отношении обработки персональных данных;
– принимать правовые, организационные и технические меры для защиты персональных данных от неправомерного или случайного доступа к ним, уничтожения, изменения, блокирования, копирования, предоставления, распространения персональных данных, а также от иных неправомерных действий в отношении персональных данных;
– прекратить передачу (распространение, предоставление, доступ) персональных данных, прекратить обработку и уничтожить персональные данные в порядке и случаях, предусмотренных Законом о персональных данных;
– исполнять иные обязанности, предусмотренные Законом о персональных данных.
4. Основные права и обязанности субъектов персональных данных
4.1. Субъекты персональных данных имеют право:
– получать информацию, касающуюся обработки его персональных данных, за исключением случаев, предусмотренных федеральными законами. Сведения предоставляются субъекту персональных данных Оператором в доступной форме, и в них не должны содержаться персональные данные, относящиеся к другим субъектам персональных данных, за исключением случаев, когда имеются законные основания для раскрытия таких персональных данных. Перечень информации и порядок ее получения установлен Законом о персональных данных;
– требовать от оператора уточнения его персональных данных, их блокирования или уничтожения в случае, если персональные данные являются неполными, устаревшими, неточными, незаконно полученными или не являются необходимыми для заявленной цели обработки, а также принимать предусмотренные законом меры по защите своих прав;
– выдвигать условие предварительного согласия при обработке персональных данных в целях продвижения на рынке товаров, работ и услуг;
– на отзыв согласия на обработку персональных данных;
– обжаловать в уполномоченный орган по защите прав субъектов персональных данных или в судебном порядке неправомерные действия или бездействие Оператора при обработке его персональных данных;
– на осуществление иных прав, предусмотренных законодательством РФ.
4.2. Субъекты персональных данных обязаны:
– предоставлять Оператору достоверные данные о себе;
– сообщать Оператору об уточнении (обновлении, изменении) своих персональных данных.
4.3. Лица, передавшие Оператору недостоверные сведения о себе, либо сведения о другом субъекте персональных данных без согласия последнего, несут ответственность в соответствии с законодательством РФ.
5. Оператор может обрабатывать следующие персональные данные Пользователя
5.1. Фамилия, имя, отчество.
5.2. Электронный адрес.
5.3. Номера телефонов.
5.4. Также на сайте происходит сбор и обработка обезличенных данных о посетителях (в т.ч. файлов «cookie») с помощью сервисов интернет-статистики (Яндекс Метрика и Гугл Аналитика и других).
5.5. Вышеперечисленные данные далее по тексту Политики объединены общим понятием Персональные данные.
5.6. Обработка специальных категорий персональных данных, касающихся расовой, национальной принадлежности, политических взглядов, религиозных или философских убеждений, интимной жизни, Оператором не осуществляется.
5.7. Обработка персональных данных, разрешенных для распространения, из числа специальных категорий персональных данных, указанных в ч. 1 ст. 10 Закона о персональных данных, допускается, если соблюдаются запреты и условия, предусмотренные ст. 10.1 Закона о персональных данных.
5.8. Согласие Пользователя на обработку персональных данных, разрешенных для распространения, оформляется отдельно от других согласий на обработку его персональных данных. При этом соблюдаются условия, предусмотренные, в частности, ст. 10.1 Закона о персональных данных. Требования к содержанию такого согласия устанавливаются уполномоченным органом по защите прав субъектов персональных данных.
5.8.1 Согласие на обработку персональных данных, разрешенных для распространения, Пользователь предоставляет Оператору непосредственно.
5.8.2 Оператор обязан в срок не позднее трех рабочих дней с момента получения указанного согласия Пользователя опубликовать информацию об условиях обработки, о наличии запретов и условий на обработку неограниченным кругом лиц персональных данных, разрешенных для распространения.
5.8.3 Передача (распространение, предоставление, доступ) персональных данных, разрешенных субъектом персональных данных для распространения, должна быть прекращена в любое время по требованию субъекта персональных данных. Данное требование должно включать в себя фамилию, имя, отчество (при наличии), контактную информацию (номер телефона, адрес электронной почты или почтовый адрес) субъекта персональных данных, а также перечень персональных данных, обработка которых подлежит прекращению. Указанные в данном требовании персональные данные могут обрабатываться только Оператором, которому оно направлено.
5.8.4 Согласие на обработку персональных данных, разрешенных для распространения, прекращает свое действие с момента поступления Оператору требования, указанного в п. 5.8.3 настоящей Политики в отношении обработки персональных данных.
6. Принципы обработки персональных данных
6.1. Обработка персональных данных осуществляется на законной и справедливой основе.
6.2. Обработка персональных данных ограничивается достижением конкретных, заранее определенных и законных целей. Не допускается обработка персональных данных, несовместимая с целями сбора персональных данных.
6.3. Не допускается объединение баз данных, содержащих персональные данные, обработка которых осуществляется в целях, несовместимых между собой.
6.4. Обработке подлежат только персональные данные, которые отвечают целям их обработки.
6.5. Содержание и объем обрабатываемых персональных данных соответствуют заявленным целям обработки. Не допускается избыточность обрабатываемых персональных данных по отношению к заявленным целям их обработки.
6.6. При обработке персональных данных обеспечивается точность персональных данных, их достаточность, а в необходимых случаях и актуальность по отношению к целям обработки персональных данных. Оператор принимает необходимые меры и/или обеспечивает их принятие по удалению или уточнению неполных или неточных данных.
6.7. Хранение персональных данных осуществляется в форме, позволяющей определить субъекта персональных данных, не дольше, чем этого требуют цели обработки персональных данных, если срок хранения персональных данных не установлен федеральным законом, договором, стороной которого, выгодоприобретателем или поручителем по которому является субъект персональных данных. Обрабатываемые персональные данные уничтожаются либо обезличиваются по достижении целей обработки или в случае утраты необходимости в достижении этих целей, если иное не предусмотрено федеральным законом.
7. Цели обработки персональных данных
7.1. Цель обработки персональных данных Пользователя:
– информирование Пользователя посредством отправки электронных писем;
– заключение, исполнение и прекращение гражданско-правовых договоров;
– предоставление доступа Пользователю к сервисам, информации и/или материалам, содержащимся на веб-сайте https://relocator.world/.
7.2. Также Оператор имеет право направлять Пользователю уведомления о новых продуктах и услугах, специальных предложениях и различных событиях. Пользователь всегда может отказаться от получения информационных сообщений, направив Оператору письмо на адрес электронной почты info@relocator.world с пометкой «Отказ от уведомлений о новых продуктах и услугах и специальных предложениях».
7.3. Обезличенные данные Пользователей, собираемые с помощью сервисов интернет-статистики, служат для сбора информации о действиях Пользователей на сайте, улучшения качества сайта и его содержания.
8. Правовые основания обработки персональных данных
8.1. Правовыми основаниями обработки персональных данных Оператором являются:
– перечислите нормативно-правовые акты, регулирующие отношения, связанные с вашей деятельностью, например, если ваша деятельность связана с информационными технологиями, в частности с созданием сайтов, то здесь можно указать Федеральный закон "Об информации, информационных технологиях и о защите информации" от 27.07.2006 N 149-ФЗ;
– уставные документы Оператора;
– договоры, заключаемые между оператором и субъектом персональных данных;
– федеральные законы, иные нормативно-правовые акты в сфере защиты персональных данных;
– согласия Пользователей на обработку их персональных данных, на обработку персональных данных, разрешенных для распространения.
8.2. Оператор обрабатывает персональные данные Пользователя только в случае их заполнения и/или отправки Пользователем самостоятельно через специальные формы, расположенные на сайте https://relocator.world/ или направленные Оператору посредством электронной почты. Заполняя соответствующие формы и/или отправляя свои персональные данные Оператору, Пользователь выражает свое согласие с данной Политикой.
8.3. Оператор обрабатывает обезличенные данные о Пользователе в случае, если это разрешено в настройках браузера Пользователя (включено сохранение файлов «cookie» и использование технологии JavaScript).
8.4. Субъект персональных данных самостоятельно принимает решение о предоставлении его персональных данных и дает согласие свободно, своей волей и в своем интересе.
9. Условия обработки персональных данных
9.1. Обработка персональных данных осуществляется с согласия субъекта персональных данных на обработку его персональных данных.
9.2. Обработка персональных данных необходима для достижения целей, предусмотренных международным договором Российской Федерации или законом, для осуществления возложенных законодательством Российской Федерации на оператора функций, полномочий и обязанностей.
9.3. Обработка персональных данных необходима для осуществления правосудия, исполнения судебного акта, акта другого органа или должностного лица, подлежащих исполнению в соответствии с законодательством Российской Федерации об исполнительном производстве.
9.4. Обработка персональных данных необходима для исполнения договора, стороной которого либо выгодоприобретателем или поручителем по которому является субъект персональных данных, а также для заключения договора по инициативе субъекта персональных данных или договора, по которому субъект персональных данных будет являться выгодоприобретателем или поручителем.
9.5. Обработка персональных данных необходима для осуществления прав и законных интересов оператора или третьих лиц либо для достижения общественно значимых целей при условии, что при этом не нарушаются права и свободы субъекта персональных данных.
9.6. Осуществляется обработка персональных данных, доступ неограниченного круга лиц к которым предоставлен субъектом персональных данных либо по его просьбе (далее – общедоступные персональные данные).
9.7. Осуществляется обработка персональных данных, подлежащих опубликованию или обязательному раскрытию в соответствии с федеральным законом.
10. Порядок сбора, хранения, передачи и других видов обработки персональных данных
Безопасность персональных данных, которые обрабатываются Оператором, обеспечивается путем реализации правовых, организационных и технических мер, необходимых для выполнения в полном объеме требований действующего законодательства в области защиты персональных данных.
10.1. Оператор обеспечивает сохранность персональных данных и принимает все возможные меры, исключающие доступ к персональным данным неуполномоченных лиц.
10.2. Персональные данные Пользователя никогда, ни при каких условиях не будут переданы третьим лицам, за исключением случаев, связанных с исполнением действующего законодательства либо в случае, если субъектом персональных данных дано согласие Оператору на передачу данных третьему лицу для исполнения обязательств по гражданско-правовому договору.
10.3. В случае выявления неточностей в персональных данных, Пользователь может актуализировать их самостоятельно, путем направления Оператору уведомление на адрес электронной почты Оператора info@relocator.world с пометкой «Актуализация персональных данных».
10.4. Срок обработки персональных данных определяется достижением целей, для которых были собраны персональные данные, если иной срок не предусмотрен договором или действующим законодательством.
Пользователь может в любой момент отозвать свое согласие на обработку персональных данных, направив Оператору уведомление посредством электронной почты на электронный адрес Оператора https://relocator.world/ с пометкой «Отзыв согласия на обработку персональных данных».
10.5. Вся информация, которая собирается сторонними сервисами, в том числе платежными системами, средствами связи и другими поставщиками услуг, хранится и обрабатывается указанными лицами (Операторами) в соответствии с их Пользовательским соглашением и Политикой конфиденциальности. Субъект персональных данных и/или Пользователь обязан самостоятельно своевременно ознакомиться с указанными документами. Оператор не несет ответственность за действия третьих лиц, в том числе указанных в настоящем пункте поставщиков услуг.
10.6. Установленные субъектом персональных данных запреты на передачу (кроме предоставления доступа), а также на обработку или условия обработки (кроме получения доступа) персональных данных, разрешенных для распространения, не действуют в случаях обработки персональных данных в государственных, общественных и иных публичных интересах, определенных законодательством РФ.
10.7. Оператор при обработке персональных данных обеспечивает конфиденциальность персональных данных.
10.8. Оператор осуществляет хранение персональных данных в форме, позволяющей определить субъекта персональных данных, не дольше, чем этого требуют цели обработки персональных данных, если срок хранения персональных данных не установлен федеральным законом, договором, стороной которого, выгодоприобретателем или поручителем по которому является субъект персональных данных.
10.9. Условием прекращения обработки персональных данных может являться достижение целей обработки персональных данных, истечение срока действия согласия субъекта персональных данных или отзыв согласия субъектом персональных данных, а также выявление неправомерной обработки персональных данных.
11. Перечень действий, производимых Оператором с полученными персональными данными
11.1. Оператор осуществляет сбор, запись, систематизацию, накопление, хранение, уточнение (обновление, изменение), извлечение, использование, передачу (распространение, предоставление, доступ), обезличивание, блокирование, удаление и уничтожение персональных данных.
11.2. Оператор осуществляет автоматизированную обработку персональных данных с получением и/или передачей полученной информации по информационно-телекоммуникационным сетям или без таковой.
12. Трансграничная передача персональных данных
12.1. Оператор до начала осуществления трансграничной передачи персональных данных обязан убедиться в том, что иностранным государством, на территорию которого предполагается осуществлять передачу персональных данных, обеспечивается надежная защита прав субъектов персональных данных.
12.2. Трансграничная передача персональных данных на территории иностранных государств, не отвечающих вышеуказанным требованиям, может осуществляться только в случае наличия согласия в письменной форме субъекта персональных данных на трансграничную передачу его персональных данных и/или исполнения договора, стороной которого является субъект персональных данных.
13. Конфиденциальность персональных данных
Оператор и иные лица, получившие доступ к персональным данным, обязаны не раскрывать третьим лицам и не распространять персональные данные без согласия субъекта персональных данных, если иное не предусмотрено федеральным законом.
14. Заключительные положения
14.1. Пользователь может получить любые разъяснения по интересующим вопросам, касающимся обработки его персональных данных, обратившись к Оператору с помощью электронной почты https://relocator.world.
14.2. В данном документе будут отражены любые изменения политики обработки персональных данных Оператором. Политика действует бессрочно до замены ее новой версией.
14.3. Актуальная версия Политики в свободном доступе расположена в сети Интернет по адресу https://relocator.world/#pilicy.
Настоящая политика обработки персональных данных составлена в соответствии с требованиями Федерального закона от 27.07.2006. №152-ФЗ «О персональных данных» (далее - Закон о персональных данных) и определяет порядок обработки персональных данных и меры по обеспечению безопасности персональных данных, предпринимаемые RELOCATOR (далее – Оператор).
1.1. Оператор ставит своей важнейшей целью и условием осуществления своей деятельности соблюдение прав и свобод человека и гражданина при обработке его персональных данных, в том числе защиты прав на неприкосновенность частной жизни, личную и семейную тайну.
1.2. Настоящая политика Оператора в отношении обработки персональных данных (далее – Политика) применяется ко всей информации, которую Оператор может получить о посетителях веб-сайта https://relocator.world.
2. Основные понятия, используемые в Политике
2.1. Автоматизированная обработка персональных данных – обработка персональных данных с помощью средств вычислительной техники.
2.2. Блокирование персональных данных – временное прекращение обработки персональных данных (за исключением случаев, если обработка необходима для уточнения персональных данных).
2.3. Веб-сайт – совокупность графических и информационных материалов, а также программ для ЭВМ и баз данных, обеспечивающих их доступность в сети интернет по сетевому адресу https://relocator.world.
2.4. Информационная система персональных данных — совокупность содержащихся в базах данных персональных данных, и обеспечивающих их обработку информационных технологий и технических средств.
2.5. Обезличивание персональных данных — действия, в результате которых невозможно определить без использования дополнительной информации принадлежность персональных данных конкретному Пользователю или иному субъекту персональных данных.
2.6. Обработка персональных данных – любое действие (операция) или совокупность действий (операций), совершаемых с использованием средств автоматизации или без использования таких средств с персональными данными, включая сбор, запись, систематизацию, накопление, хранение, уточнение (обновление, изменение), извлечение, использование, передачу (распространение, предоставление, доступ), обезличивание, блокирование, удаление, уничтожение персональных данных.
2.7. Оператор – государственный орган, муниципальный орган, юридическое или физическое лицо, самостоятельно или совместно с другими лицами организующие и (или) осуществляющие обработку персональных данных, а также определяющие цели обработки персональных данных, состав персональных данных, подлежащих обработке, действия (операции), совершаемые с персональными данными.
2.8. Персональные данные – любая информация, относящаяся прямо или косвенно к определенному или определяемому Пользователю веб-сайта https://relocator.world/.
2.9. Персональные данные, разрешенные субъектом персональных данных для распространения, - персональные данные, доступ неограниченного круга лиц к которым предоставлен субъектом персональных данных путем дачи согласия на обработку персональных данных, разрешенных субъектом персональных данных для распространения в порядке, предусмотренном Законом о персональных данных (далее - персональные данные, разрешенные для распространения).
2.10. Пользователь – любой посетитель веб-сайта https://relocator.world/.
2.11. Предоставление персональных данных – действия, направленные на раскрытие персональных данных определенному лицу или определенному кругу лиц.
2.12. Распространение персональных данных – любые действия, направленные на раскрытие персональных данных неопределенному кругу лиц (передача персональных данных) или на ознакомление с персональными данными неограниченного круга лиц, в том числе обнародование персональных данных в средствах массовой информации, размещение в информационно-телекоммуникационных сетях или предоставление доступа к персональным данным каким-либо иным способом.
2.13. Трансграничная передача персональных данных – передача персональных данных на территорию иностранного государства органу власти иностранного государства, иностранному физическому или иностранному юридическому лицу.
2.14. Уничтожение персональных данных – любые действия, в результате которых персональные данные уничтожаются безвозвратно с невозможностью дальнейшего восстановления содержания персональных данных в информационной системе персональных данных и (или) уничтожаются материальные носители персональных данных.
3. Основные права и обязанности Оператора
3.1. Оператор имеет право:
– получать от субъекта персональных данных достоверные информацию и/или документы, содержащие персональные данные;
– в случае отзыва субъектом персональных данных согласия на обработку персональных данных Оператор вправе продолжить обработку персональных данных без согласия субъекта персональных данных при наличии оснований, указанных в Законе о персональных данных;
– самостоятельно определять состав и перечень мер, необходимых и достаточных для обеспечения выполнения обязанностей, предусмотренных Законом о персональных данных и принятыми в соответствии с ним нормативными правовыми актами, если иное не предусмотрено Законом о персональных данных или другими федеральными законами.
3.2. Оператор обязан:
– предоставлять субъекту персональных данных по его просьбе информацию, касающуюся обработки его персональных данных;
– организовывать обработку персональных данных в порядке, установленном действующим законодательством РФ;
– отвечать на обращения и запросы субъектов персональных данных и их законных представителей в соответствии с требованиями Закона о персональных данных;
– сообщать в уполномоченный орган по защите прав субъектов персональных данных по запросу этого органа необходимую информацию в течение 30 дней с даты получения такого запроса;
– публиковать или иным образом обеспечивать неограниченный доступ к настоящей Политике в отношении обработки персональных данных;
– принимать правовые, организационные и технические меры для защиты персональных данных от неправомерного или случайного доступа к ним, уничтожения, изменения, блокирования, копирования, предоставления, распространения персональных данных, а также от иных неправомерных действий в отношении персональных данных;
– прекратить передачу (распространение, предоставление, доступ) персональных данных, прекратить обработку и уничтожить персональные данные в порядке и случаях, предусмотренных Законом о персональных данных;
– исполнять иные обязанности, предусмотренные Законом о персональных данных.
4. Основные права и обязанности субъектов персональных данных
4.1. Субъекты персональных данных имеют право:
– получать информацию, касающуюся обработки его персональных данных, за исключением случаев, предусмотренных федеральными законами. Сведения предоставляются субъекту персональных данных Оператором в доступной форме, и в них не должны содержаться персональные данные, относящиеся к другим субъектам персональных данных, за исключением случаев, когда имеются законные основания для раскрытия таких персональных данных. Перечень информации и порядок ее получения установлен Законом о персональных данных;
– требовать от оператора уточнения его персональных данных, их блокирования или уничтожения в случае, если персональные данные являются неполными, устаревшими, неточными, незаконно полученными или не являются необходимыми для заявленной цели обработки, а также принимать предусмотренные законом меры по защите своих прав;
– выдвигать условие предварительного согласия при обработке персональных данных в целях продвижения на рынке товаров, работ и услуг;
– на отзыв согласия на обработку персональных данных;
– обжаловать в уполномоченный орган по защите прав субъектов персональных данных или в судебном порядке неправомерные действия или бездействие Оператора при обработке его персональных данных;
– на осуществление иных прав, предусмотренных законодательством РФ.
4.2. Субъекты персональных данных обязаны:
– предоставлять Оператору достоверные данные о себе;
– сообщать Оператору об уточнении (обновлении, изменении) своих персональных данных.
4.3. Лица, передавшие Оператору недостоверные сведения о себе, либо сведения о другом субъекте персональных данных без согласия последнего, несут ответственность в соответствии с законодательством РФ.
5. Оператор может обрабатывать следующие персональные данные Пользователя
5.1. Фамилия, имя, отчество.
5.2. Электронный адрес.
5.3. Номера телефонов.
5.4. Также на сайте происходит сбор и обработка обезличенных данных о посетителях (в т.ч. файлов «cookie») с помощью сервисов интернет-статистики (Яндекс Метрика и Гугл Аналитика и других).
5.5. Вышеперечисленные данные далее по тексту Политики объединены общим понятием Персональные данные.
5.6. Обработка специальных категорий персональных данных, касающихся расовой, национальной принадлежности, политических взглядов, религиозных или философских убеждений, интимной жизни, Оператором не осуществляется.
5.7. Обработка персональных данных, разрешенных для распространения, из числа специальных категорий персональных данных, указанных в ч. 1 ст. 10 Закона о персональных данных, допускается, если соблюдаются запреты и условия, предусмотренные ст. 10.1 Закона о персональных данных.
5.8. Согласие Пользователя на обработку персональных данных, разрешенных для распространения, оформляется отдельно от других согласий на обработку его персональных данных. При этом соблюдаются условия, предусмотренные, в частности, ст. 10.1 Закона о персональных данных. Требования к содержанию такого согласия устанавливаются уполномоченным органом по защите прав субъектов персональных данных.
5.8.1 Согласие на обработку персональных данных, разрешенных для распространения, Пользователь предоставляет Оператору непосредственно.
5.8.2 Оператор обязан в срок не позднее трех рабочих дней с момента получения указанного согласия Пользователя опубликовать информацию об условиях обработки, о наличии запретов и условий на обработку неограниченным кругом лиц персональных данных, разрешенных для распространения.
5.8.3 Передача (распространение, предоставление, доступ) персональных данных, разрешенных субъектом персональных данных для распространения, должна быть прекращена в любое время по требованию субъекта персональных данных. Данное требование должно включать в себя фамилию, имя, отчество (при наличии), контактную информацию (номер телефона, адрес электронной почты или почтовый адрес) субъекта персональных данных, а также перечень персональных данных, обработка которых подлежит прекращению. Указанные в данном требовании персональные данные могут обрабатываться только Оператором, которому оно направлено.
5.8.4 Согласие на обработку персональных данных, разрешенных для распространения, прекращает свое действие с момента поступления Оператору требования, указанного в п. 5.8.3 настоящей Политики в отношении обработки персональных данных.
6. Принципы обработки персональных данных
6.1. Обработка персональных данных осуществляется на законной и справедливой основе.
6.2. Обработка персональных данных ограничивается достижением конкретных, заранее определенных и законных целей. Не допускается обработка персональных данных, несовместимая с целями сбора персональных данных.
6.3. Не допускается объединение баз данных, содержащих персональные данные, обработка которых осуществляется в целях, несовместимых между собой.
6.4. Обработке подлежат только персональные данные, которые отвечают целям их обработки.
6.5. Содержание и объем обрабатываемых персональных данных соответствуют заявленным целям обработки. Не допускается избыточность обрабатываемых персональных данных по отношению к заявленным целям их обработки.
6.6. При обработке персональных данных обеспечивается точность персональных данных, их достаточность, а в необходимых случаях и актуальность по отношению к целям обработки персональных данных. Оператор принимает необходимые меры и/или обеспечивает их принятие по удалению или уточнению неполных или неточных данных.
6.7. Хранение персональных данных осуществляется в форме, позволяющей определить субъекта персональных данных, не дольше, чем этого требуют цели обработки персональных данных, если срок хранения персональных данных не установлен федеральным законом, договором, стороной которого, выгодоприобретателем или поручителем по которому является субъект персональных данных. Обрабатываемые персональные данные уничтожаются либо обезличиваются по достижении целей обработки или в случае утраты необходимости в достижении этих целей, если иное не предусмотрено федеральным законом.
7. Цели обработки персональных данных
7.1. Цель обработки персональных данных Пользователя:
– информирование Пользователя посредством отправки электронных писем;
– заключение, исполнение и прекращение гражданско-правовых договоров;
– предоставление доступа Пользователю к сервисам, информации и/или материалам, содержащимся на веб-сайте https://relocator.world/.
7.2. Также Оператор имеет право направлять Пользователю уведомления о новых продуктах и услугах, специальных предложениях и различных событиях. Пользователь всегда может отказаться от получения информационных сообщений, направив Оператору письмо на адрес электронной почты info@relocator.world с пометкой «Отказ от уведомлений о новых продуктах и услугах и специальных предложениях».
7.3. Обезличенные данные Пользователей, собираемые с помощью сервисов интернет-статистики, служат для сбора информации о действиях Пользователей на сайте, улучшения качества сайта и его содержания.
8. Правовые основания обработки персональных данных
8.1. Правовыми основаниями обработки персональных данных Оператором являются:
– перечислите нормативно-правовые акты, регулирующие отношения, связанные с вашей деятельностью, например, если ваша деятельность связана с информационными технологиями, в частности с созданием сайтов, то здесь можно указать Федеральный закон "Об информации, информационных технологиях и о защите информации" от 27.07.2006 N 149-ФЗ;
– уставные документы Оператора;
– договоры, заключаемые между оператором и субъектом персональных данных;
– федеральные законы, иные нормативно-правовые акты в сфере защиты персональных данных;
– согласия Пользователей на обработку их персональных данных, на обработку персональных данных, разрешенных для распространения.
8.2. Оператор обрабатывает персональные данные Пользователя только в случае их заполнения и/или отправки Пользователем самостоятельно через специальные формы, расположенные на сайте https://relocator.world/ или направленные Оператору посредством электронной почты. Заполняя соответствующие формы и/или отправляя свои персональные данные Оператору, Пользователь выражает свое согласие с данной Политикой.
8.3. Оператор обрабатывает обезличенные данные о Пользователе в случае, если это разрешено в настройках браузера Пользователя (включено сохранение файлов «cookie» и использование технологии JavaScript).
8.4. Субъект персональных данных самостоятельно принимает решение о предоставлении его персональных данных и дает согласие свободно, своей волей и в своем интересе.
9. Условия обработки персональных данных
9.1. Обработка персональных данных осуществляется с согласия субъекта персональных данных на обработку его персональных данных.
9.2. Обработка персональных данных необходима для достижения целей, предусмотренных международным договором Российской Федерации или законом, для осуществления возложенных законодательством Российской Федерации на оператора функций, полномочий и обязанностей.
9.3. Обработка персональных данных необходима для осуществления правосудия, исполнения судебного акта, акта другого органа или должностного лица, подлежащих исполнению в соответствии с законодательством Российской Федерации об исполнительном производстве.
9.4. Обработка персональных данных необходима для исполнения договора, стороной которого либо выгодоприобретателем или поручителем по которому является субъект персональных данных, а также для заключения договора по инициативе субъекта персональных данных или договора, по которому субъект персональных данных будет являться выгодоприобретателем или поручителем.
9.5. Обработка персональных данных необходима для осуществления прав и законных интересов оператора или третьих лиц либо для достижения общественно значимых целей при условии, что при этом не нарушаются права и свободы субъекта персональных данных.
9.6. Осуществляется обработка персональных данных, доступ неограниченного круга лиц к которым предоставлен субъектом персональных данных либо по его просьбе (далее – общедоступные персональные данные).
9.7. Осуществляется обработка персональных данных, подлежащих опубликованию или обязательному раскрытию в соответствии с федеральным законом.
10. Порядок сбора, хранения, передачи и других видов обработки персональных данных
Безопасность персональных данных, которые обрабатываются Оператором, обеспечивается путем реализации правовых, организационных и технических мер, необходимых для выполнения в полном объеме требований действующего законодательства в области защиты персональных данных.
10.1. Оператор обеспечивает сохранность персональных данных и принимает все возможные меры, исключающие доступ к персональным данным неуполномоченных лиц.
10.2. Персональные данные Пользователя никогда, ни при каких условиях не будут переданы третьим лицам, за исключением случаев, связанных с исполнением действующего законодательства либо в случае, если субъектом персональных данных дано согласие Оператору на передачу данных третьему лицу для исполнения обязательств по гражданско-правовому договору.
10.3. В случае выявления неточностей в персональных данных, Пользователь может актуализировать их самостоятельно, путем направления Оператору уведомление на адрес электронной почты Оператора info@relocator.world с пометкой «Актуализация персональных данных».
10.4. Срок обработки персональных данных определяется достижением целей, для которых были собраны персональные данные, если иной срок не предусмотрен договором или действующим законодательством.
Пользователь может в любой момент отозвать свое согласие на обработку персональных данных, направив Оператору уведомление посредством электронной почты на электронный адрес Оператора https://relocator.world/ с пометкой «Отзыв согласия на обработку персональных данных».
10.5. Вся информация, которая собирается сторонними сервисами, в том числе платежными системами, средствами связи и другими поставщиками услуг, хранится и обрабатывается указанными лицами (Операторами) в соответствии с их Пользовательским соглашением и Политикой конфиденциальности. Субъект персональных данных и/или Пользователь обязан самостоятельно своевременно ознакомиться с указанными документами. Оператор не несет ответственность за действия третьих лиц, в том числе указанных в настоящем пункте поставщиков услуг.
10.6. Установленные субъектом персональных данных запреты на передачу (кроме предоставления доступа), а также на обработку или условия обработки (кроме получения доступа) персональных данных, разрешенных для распространения, не действуют в случаях обработки персональных данных в государственных, общественных и иных публичных интересах, определенных законодательством РФ.
10.7. Оператор при обработке персональных данных обеспечивает конфиденциальность персональных данных.
10.8. Оператор осуществляет хранение персональных данных в форме, позволяющей определить субъекта персональных данных, не дольше, чем этого требуют цели обработки персональных данных, если срок хранения персональных данных не установлен федеральным законом, договором, стороной которого, выгодоприобретателем или поручителем по которому является субъект персональных данных.
10.9. Условием прекращения обработки персональных данных может являться достижение целей обработки персональных данных, истечение срока действия согласия субъекта персональных данных или отзыв согласия субъектом персональных данных, а также выявление неправомерной обработки персональных данных.
11. Перечень действий, производимых Оператором с полученными персональными данными
11.1. Оператор осуществляет сбор, запись, систематизацию, накопление, хранение, уточнение (обновление, изменение), извлечение, использование, передачу (распространение, предоставление, доступ), обезличивание, блокирование, удаление и уничтожение персональных данных.
11.2. Оператор осуществляет автоматизированную обработку персональных данных с получением и/или передачей полученной информации по информационно-телекоммуникационным сетям или без таковой.
12. Трансграничная передача персональных данных
12.1. Оператор до начала осуществления трансграничной передачи персональных данных обязан убедиться в том, что иностранным государством, на территорию которого предполагается осуществлять передачу персональных данных, обеспечивается надежная защита прав субъектов персональных данных.
12.2. Трансграничная передача персональных данных на территории иностранных государств, не отвечающих вышеуказанным требованиям, может осуществляться только в случае наличия согласия в письменной форме субъекта персональных данных на трансграничную передачу его персональных данных и/или исполнения договора, стороной которого является субъект персональных данных.
13. Конфиденциальность персональных данных
Оператор и иные лица, получившие доступ к персональным данным, обязаны не раскрывать третьим лицам и не распространять персональные данные без согласия субъекта персональных данных, если иное не предусмотрено федеральным законом.
14. Заключительные положения
14.1. Пользователь может получить любые разъяснения по интересующим вопросам, касающимся обработки его персональных данных, обратившись к Оператору с помощью электронной почты https://relocator.world.
14.2. В данном документе будут отражены любые изменения политики обработки персональных данных Оператором. Политика действует бессрочно до замены ее новой версией.
14.3. Актуальная версия Политики в свободном доступе расположена в сети Интернет по адресу https://relocator.world/#pilicy.
GET IT FOR FREE
ANONYMOUS CONSULTATION
Anonymous and confidential




